MVNOs are providers of mobile communication services that have their own customer base but not their own telecom infrastructure. In order to offer these services, they lease and use the network of a mobile telecom operator.
A broad range of operational models were tested, from the lightweight “reseller” MVNO that essentially re-sells minutes/SMSs/data bought from an MNO, through to the “thick” or “full service” MVNO that operates its own customer care, billing system and even parts of the core network.
MVNOs may also be classified according to their customer business model; they concentrate on specific market segments: low-cost, youth, business or ethnic categories.
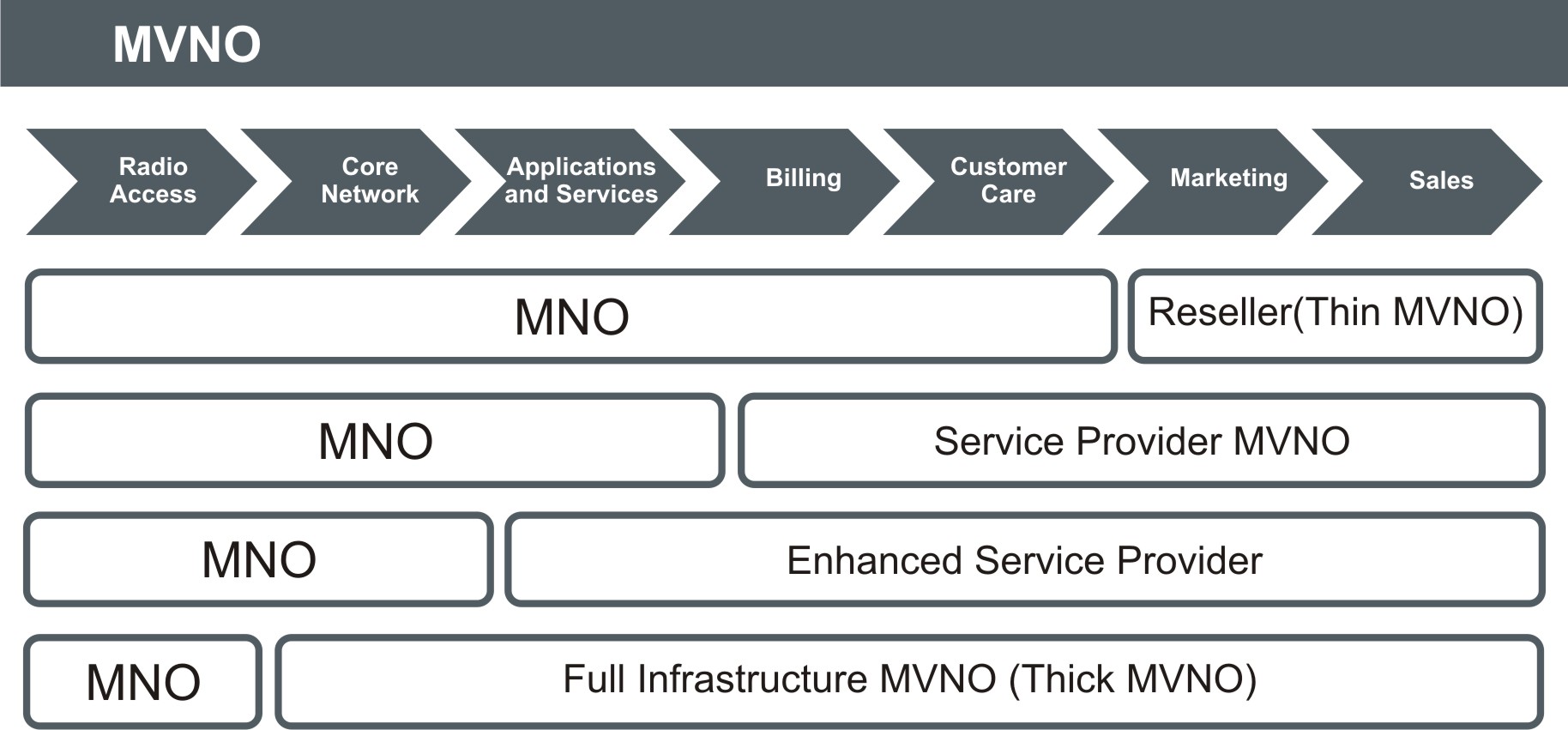
Reseller MVNOs
They usually have a well known brand and a complex retail infrastructure and focus on sales and on leveraging customer relationships. They resell services on margins, the pricing being agreed with the MNO. They have control over their sales and marketing processes, but they usually differentiate only on pricing, brand identity and value.
Service provider MVNOs
Supplementary to the reseller, the service provider MVNOs manage all customer care processes, including the CRM, customer support, self care and billing processes from flexible account lifecycle, complex tariff bundles and packages, voice, data and SMS services. The Service provider model suits businesses with brands or service concepts that differentiate them from existing players
Enhanced Service Providers
In addition to their own billing and customer care processes, enhanced service providers usually have their own infrastructure which allows them to have complete control over their business and service offerings. The enhanced service providers usually run their own value added services platforms such as voicemail, missed call notification, VPN. Having their own infrastructure, MVNOs become serious competitors for MNO in terms of price and service offerings.
